
Hydraulic Hoses vs. Pneumatic Hoses: Understanding the Differences
Many industries rely on hydraulic and/or pneumatic hoses to operate their systems or machinery. But it’s a mistake to think that all hoses are created equal and interchangeable. There are almost as many different varieties of hose as there are types of applications. Understanding the differences between hydraulic hoses and pneumatic hoses is important for everyone, including buyers, engineers, and mechanics, as each has unique features and functions. In this article, we address the topic of hydraulic hoses vs. pneumatic hoses, taking a look at the fundamental differences between them so that you can make informed decisions to ensure the reliability, durability, and safety of your system or equipment.
Quick Links
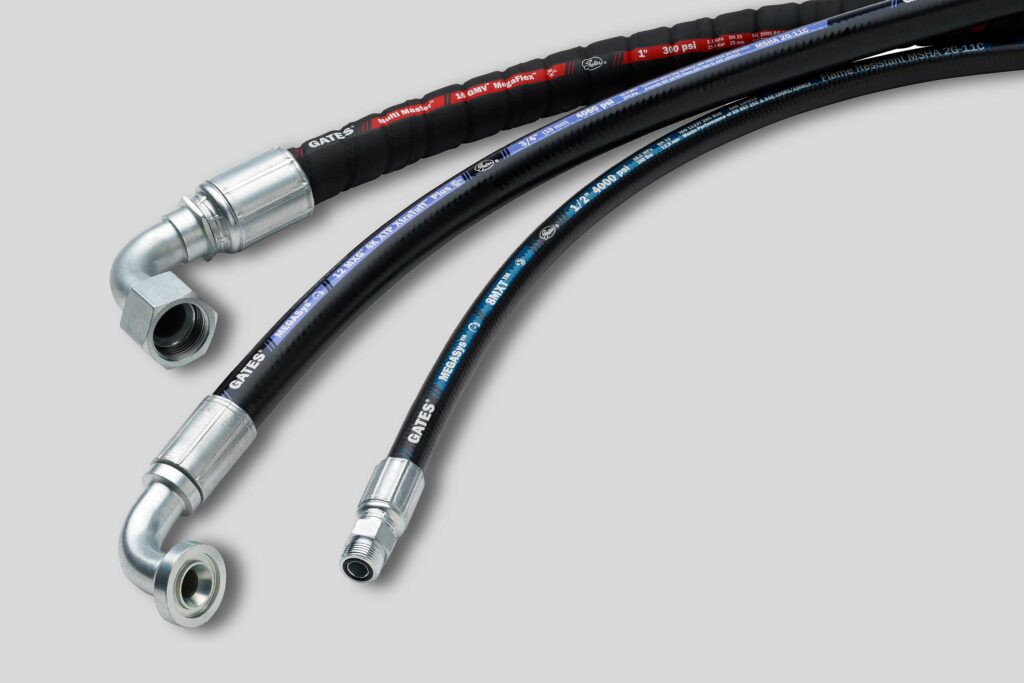

What is a hydraulic hose?
A hydraulic hose is a flexible conduit meticulously engineered to transport pressurized fluid within hydraulic systems. These hoses are indispensable for transferring mechanical power in a vast array of machinery and equipment, prominently utilized across diverse sectors such as construction, manufacturing, and automotive industries.
The anatomy of a hydraulic hose includes an inner tube that directly carries the hydraulic fluid. This tube is critically reinforced with multiple layers, typically made from high-strength materials like steel wire or synthetic fibers, to withstand the high pressures encountered in hydraulic applications. Additionally, an outer cover, often made from durable materials like rubber or thermoplastic, encases these layers, offering essential protection against external wear, abrasion, and environmental factors.
This robust construction not only ensures the efficient and safe conveyance of hydraulic fluids but also contributes to the longevity and reliability of hydraulic hoses in demanding industrial settings.
What is a pneumatic hose?
Pneumatic hoses are specially crafted for use in pneumatic systems, where they play a crucial role in transferring compressed air or gas. These hoses are key components in a variety of industries, including automation, where they control machinery, mining for powering heavy-duty drills and ventilation systems, and even in dentistry for operating precision tools. Other common examples include air brakes, exercise equipment, air compressors, and jackhammers.
Like their hydraulic counterparts, pneumatic hoses comprise an inner tube, which is the primary conduit for the air or gas. This tube is made from flexible materials which are sometimes reinforced with layers that may include fabric, wire, or a combination of both, to provide increased strength and prevent collapse under pressure. The outer cover of these hoses is designed to be resistant to abrasion, chemicals, and environmental factors, ensuring a long service life.
The materials and construction of pneumatic hoses are specifically chosen to cater to the unique requirements of air or gas transfer, focusing on aspects like flexibility, weight, and pressure handling, which differ significantly from those of hydraulic systems. This careful design ensures that pneumatic hoses can efficiently and safely handle the demands of the applications they are used in.
Hydraulic hoses vs. pneumatic hoses: The Key differences
Hydraulic and pneumatic hoses each have their own characteristics, making one hose better suited to one application than another. Let’s take a look at the main differences between hydraulic hoses and pneumatic hoses.
Medium (fluid versus gases)
Hydraulic Hoses: Hydraulic hoses are integral in transporting hydraulic fluids, which are the lifeblood of hydraulic systems, playing a crucial role in power transmission and control in various machinery and equipment.
Pneumatic Hoses: These hoses are designed to efficiently transport compressed air or gases, which are key to powering a wide range of pneumatic tools and machinery in numerous industrial and commercial applications.
Construction & materials
Hydraulic Hoses: Commonly constructed from durable synthetic rubber or thermoplastics, hydraulic hoses feature multiple reinforcement layers, such as steel wire or textile, providing the necessary strength to withstand high-pressure applications commonly found in hydraulic systems.
Pneumatic Hoses: These hoses are often made from materials like polyurethane, PVC, polyethylene, nylon, polypropylene, and PTFE, chosen for their ability to provide greater flexibility and a lighter weight, which is essential for the dynamic requirements of pneumatic systems, where ease of movement and handling are crucial.
Size & flexibility
Hydraulic Hoses: Typically larger in diameter, hydraulic hoses are designed to handle high flow rates and intense pressure, but their robust reinforcement layers can result in reduced flexibility.
Pneumatic Hoses: Generally featuring a smaller diameter, pneumatic hoses are more flexible, which aids in efficient maneuverability and minimizes the loss of air or gas volume and pressure during operation.
Pressure ratings
Hydraulic Hoses: Specifically engineered for high-pressure applications, hydraulic hoses are capable of withstanding intense forces, often handling pressures up to 5000 psi or higher in some hydraulic systems. This high-pressure capacity is essential for the efficient functioning of heavy machinery and industrial applications.
Pneumatic Hoses: In contrast, pneumatic hoses typically have lower pressure ratings, as the systems they serve operate at reduced pressures. These hoses generally handle pressures in the range of 100 to 150 psi, which is sufficient for the compressed air or gas flow in most pneumatic tools and equipment.
Temperature
Hydraulic Hoses: Hydraulic hoses are designed to endure a broad spectrum of temperatures, often ranging from -40°F to +250°F (-40°C to +121°C). This wide range is necessary due to the significant heat generated by hydraulic fluids under high pressure, ensuring the hose maintains its integrity and performance even in extreme thermal environments.
Pneumatic Hoses: The temperature requirements for pneumatic hoses are generally less demanding, with typical operating ranges from -20°F to +180°F (-29°C to +82°C). This is because the compressed air or gases they carry usually have lower temperature profiles, reducing the thermal stress on the hose materials and structure.
Flow rate and velocity
Hydraulic Hoses: Hydraulic hoses are designed to transport fluid at relatively slower speeds. This is primarily because the fluids they carry, like hydraulic oil, have higher viscosity compared to air. The benefit of this slower flow rate is a reduction in the likelihood of wear and tear within the hose, enhancing its longevity and reliability.
Pneumatic Hoses: Pneumatic hoses typically operate at higher velocities. This is due to the lower viscosity of gases, such as air, which these hoses transport. While this can be efficient, the higher velocity also poses a risk of increased wear and tear. Therefore, proper management and maintenance are crucial to prevent rapid deterioration of pneumatic hoses.
End fittings
Hydraulic Hoses: Hydraulic hoses require robust fittings to handle high pressures. These fittings are typically crimped or swaged and are permanently attached to the pipe using a special tool. The end fittings of a hydraulic hose assembly are normally threaded or flanged to ensure a secure and leak-free connection.
Pneumatic Hoses: Fittings of pneumatic hoses are less complex, reflecting the lower pressures in pneumatic systems. They are often push-in fittings, which can be easily attached or removed by hand.
Interchangeability of hydraulic and pneumatic hoses
The interchangeability of hydraulic and pneumatic hoses is a complex issue often misunderstood in various industries. At first glance, these hoses might appear similar, but their fundamental differences in construction and pressure handling capabilities make them unsuitable for interchangeable use. Hydraulic hoses are designed to withstand high-pressure environments typically associated with fluid power systems, whereas pneumatic hoses are tailored for lower-pressure air or gas systems.
Using a pneumatic hose in a hydraulic system could lead to a catastrophic failure due to the hose’s inability to handle high pressures. Similarly, employing a hydraulic hose in a pneumatic setup might not yield optimal results due to its reduced flexibility and larger diameter, potentially affecting the system’s efficiency and maneuverability. Moreover, the risk of system failures extends beyond mere operational inefficiency; it can pose significant safety hazards, including hose ruptures, leaks, and machinery malfunctions.
These risks underscore the importance of selecting the correct hose type for each specific application and adhering to industry standards and manufacturer specifications to ensure system integrity and operator safety.
In conclusion
Understanding the differences between hydraulic hoses and pneumatic hoses is crucial for the safe and efficient operation of fluid power systems. These differences in construction, pressure ratings, medium, temperature, size, flow rate, velocity, and flexibility dictate their specific applications in various industries. Choosing the right type of hose is vital for system integrity and performance.
Marshall Equipment is your go-to distributor for hydraulic, pneumatic, and industrial hoses and fittings in Eastern Canada. Our extensive selection ensures you find the perfect hydraulic hose or pneumatic hose for your needs. We also offer expert custom hose assembly services. Contact our team of experts for guidance and solutions tailored to your system’s requirements.






Follow Us